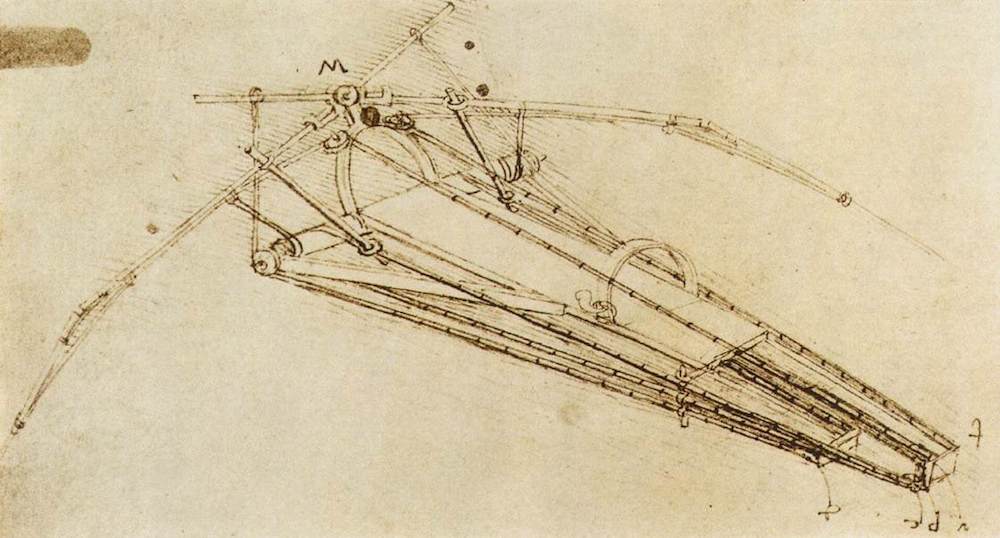
Leonardo da Vinci was said to be one of the greatest engineers of his time. During his engineering years, one of his most promising inventions was the revolutionary flying machine. The flying machine was unlike anything anyone had ever seen before.
It had a 33-foot wingspan and resembled a bird. The most unique feature of the machine was its piloting feature. Pilots would lie down in the machine between the wings and pilot it using a hand crank with a rod-and-pulley system. The lightweight membrane made to cover the frame of the flying machine was made from pine and raw silk.
On February 3, 1946, the day of the test, the flying machine test failed.
The flying machine didn’t work because of a flawed design. However, there has been much speculation surrounding the failed test. Many believed da Vinci may have purposely failed the test to keep his flying machine from being used for military use. People still wonder if there is truth to the rumors since he later fled the country in protest of military policies.
Born April 15, 1452, in the High Renaissance era, Leonardo da Vinci was a multi-talented engineer. His birthplace is Anciano, Italy. Da Vinci had many talents and professions during his lifetime. He was a painter, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. His most famous paintings include the Mona Lisa painted in 1503 and the Last Supper painted in 1498.
Leonardo da Vinci died on May 2, 1519, in France.