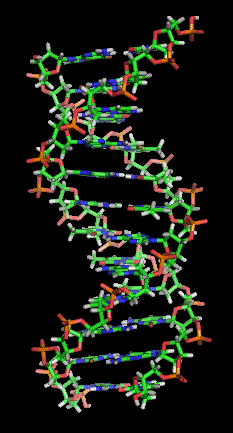
On this day in 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick published a brief but groundbreaking paper in *Nature* that revealed the double helix structure of DNA. This discovery answered fundamental questions about biology and heredity, transforming our understanding of the building blocks of life.
Their model explained how genetic information is stored and replicated, which established the foundation for modern genetics, biotechnology, and forensic science. This was not merely a scientific breakthrough; it marked the beginning of a new era in medicine and biology. Their discovery revealed the mystery of how genetic information is stored, transferred, and replicated in living organisms. This understanding has led to significant advancements in the diagnosis, treatment, and knowledge of diseases.
Watson and Crick’s model described DNA as two strands wound around each other, forming a double helix, with complementary base pairs (adenine with thymine, and guanine with cytosine) connecting the strands like rungs on a twisted ladder. This elegant structure, with its unique shape and base-pairing rules, explained both the stability of genetic material and how it could be copied – a critical key to understanding heredity.
The discovery was a culmination of the work of many other scientists, including Rosalind Franklin, whose X-ray diffraction images of DNA provided crucial insights. Although Franklin’s contributions weren’t fully acknowledged at the time, her work has since received long-overdue recognition. This collaborative effort underscores the importance of shared knowledge and the collective pursuit of scientific understanding.
Watson and Crick’s breakthrough ushered in the era of molecular biology, paving the way for significant advances, including genetic engineering, DNA fingerprinting, the Human Genome Project, and gene therapy.
Fun Facts:
- This discovery was published in the Nature journal on April 25, 1953
- Watson and Crick described the structure of DNA as a double helix with base-pairing rules
- Other key contributors included Rosalind Franklin, whose X-ray images were vital
- Impact: Revolutionized biology, genetics, medicine, and biotechnology
- The original paper was only one page long, yet it’s one of the most influential scientific documents ever published.